Overview
Rain Garden Soil is designed to manage stormwater much like bioretention soils; however, they are generally used in smaller scale applications with more ornamental and visually pleasing plantings. This is because rain gardens are often located close to and around buildings and are integrated into the larger aesthetic landscape design. These smaller scale features are a more convenient choice for old sites that are required to upgrade their stormwater infrastructure to meet current building and zoning codes. Rain Gardens are effective because they can be implemented in multiple small installations interspersed in multiple locations around a property that collectively capture the total volume of displaced stormwater.
A stormwater management plan is now a requirement with all new construction that creates impervious surfaces. Water must be contained on site or at least slowed down to prevent flooding and pollution. Bioretention basins are part of the building code and are required for most all building projects including renovations and expansions. The understanding and design of these soils is evolving rapidly.
Other industry names used are Bio-soil, Stormwater Soil, Filter Media, Amended Soil, Engineered Soil.
Questions about our products?

Ingredients
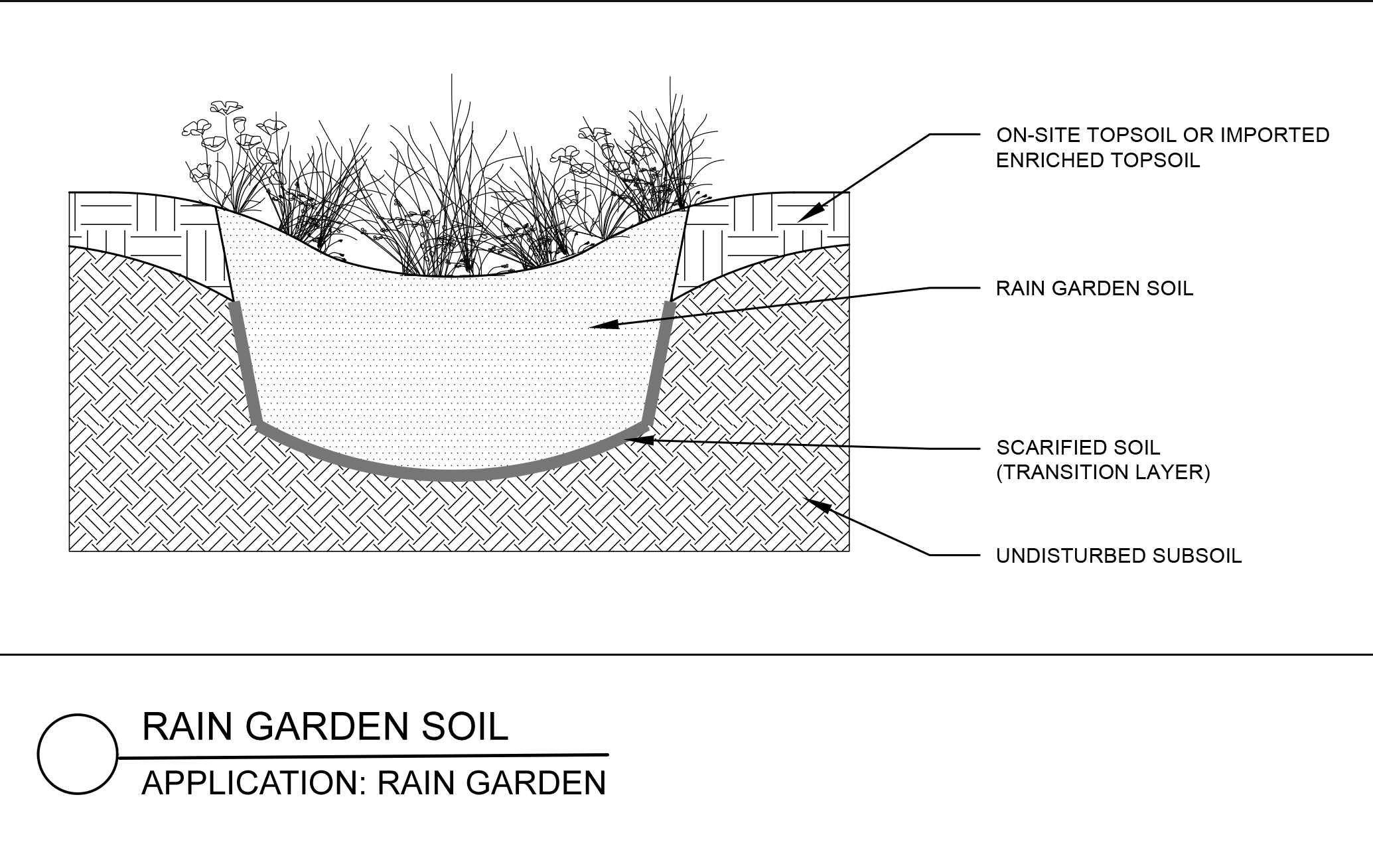
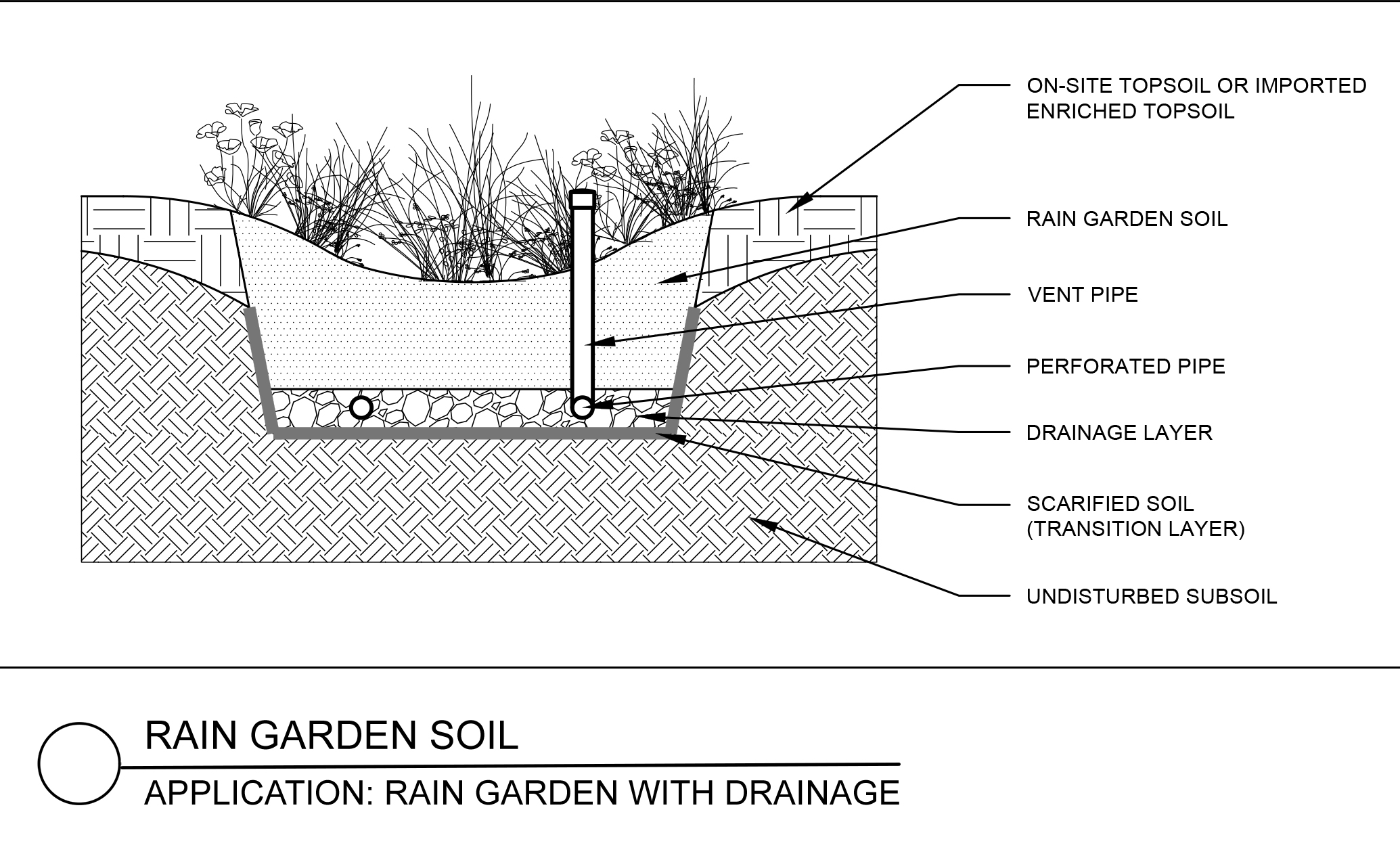
Generally containing a mix of sand, compost, soil or mulch, Rain Garden Soils are designed to meet many specific performance parameters including soil particle size gradation, infiltration rate, pH and organic matter content. Rain gardens are sometimes designed as whole systems where they are coupled with underdrainage for enhanced performance. Information and design of rain garden and bioretention soils is evolving rapidly. Laurel Valley Soils is happy to offer guidance for Engineers and Landscape Architects in the development or selection of specific rain garden soil solutions and specifications.
Analytical
Rain Garden Soil is generally light brown in color, has a light bulk density, and can feel spongy. Often on the sandy side and sometimes containing mulch, these soils generally have a neutral pH range and an average 5% organic matter content by weight. Most projects specifying Rain Garden Soil will provide a specification with specific parameter ranges for the various elements that combined provide the functionality of the mix. Laurel Valley will assist with the submission process by providing test reports, conducting new testing if required and interfacing with project engineers though out the approval process as needed. If a specification is not provided, Laurel Valley can offer advice as well as many off the shelf mix options.
Benefits
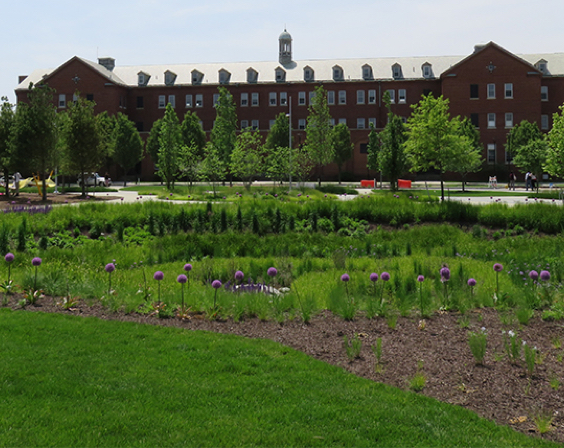
Rain Garden Soil captures, infiltrates, and filters stormwater. It supports plantings that assist with this process while providing ecologically friendly wildlife habitats. Rain Gardens are also designed to be aesthetically pleasing and can be an asset improving the landscape.
Benefits at a Glance
- Organic Matter
- Nutrients
- Biology
- Water Holding Capacity
- Improves Soil Structure and Porosity
Applications
Rain Garden Soils are often installed in depths ranging from 12-48″. The deeper medias are often installed in lifts that are lightly compacted. The best way to install Rain Garden Soil when site conditions allow is to use an excavator from outside the basin, a telebelt or slinger truck.
See our soils at work